Structural Heart
Pre-procedural planning
Successful structural heart interventions require innovation to navigate the high risks and complexity. 3D-CT planning and 3D printing reveal unprecedented insights while preparing for structural heart interventions. The adoption of 3D in the modern medical setting is inevitable — bringing clarity to complexity with these technologies.
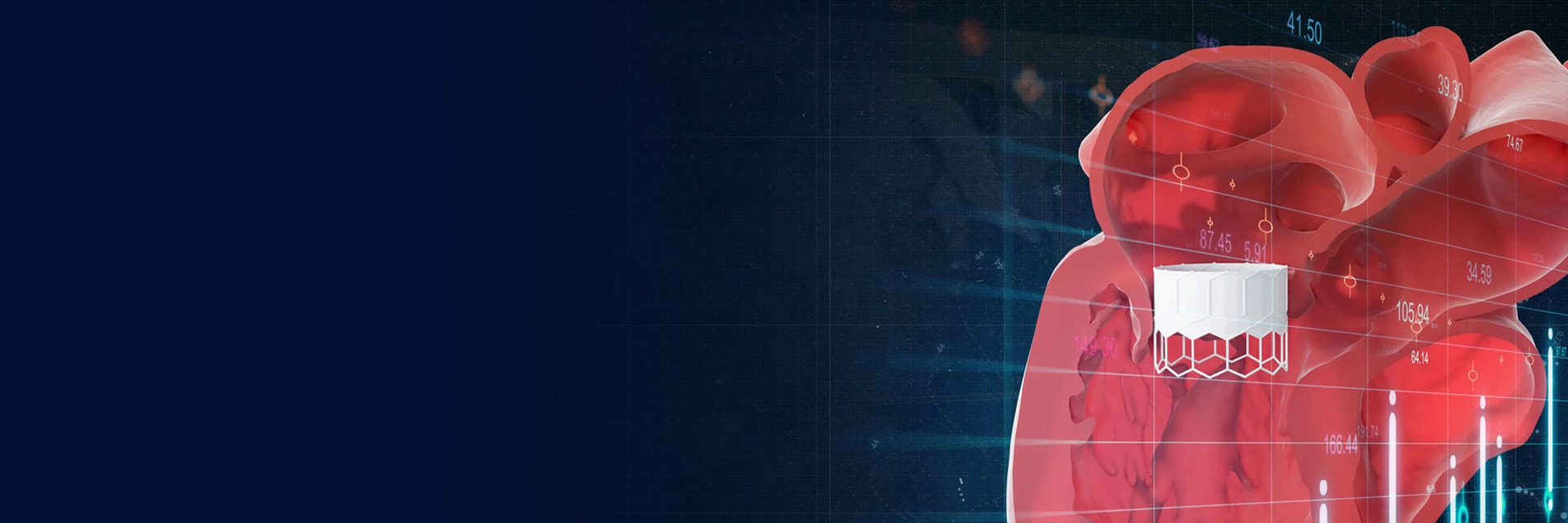

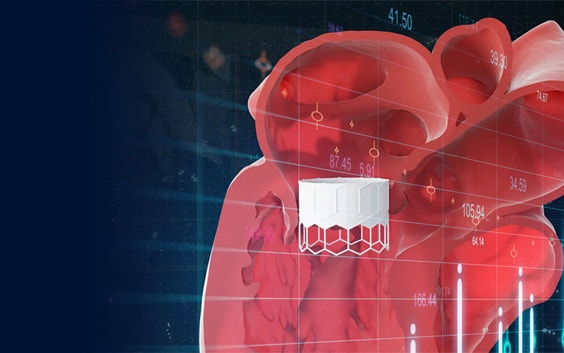
Benefits
Reliably estimate risk
Harness accurate measurements and improved insights on anatomy to reliably estimate transcatheter procedure risks for each patient.
Enter procedures with confidence
Optimally and virtually plan procedures with reliable measurements, enhanced 3D insights, online case sharing capabilities, and 3D prints.
Provide care quickly
Leverage automation to execute efficient and intuitive planning. Gain control by pre-screening with tools in hand and speed up patient eligibility evaluation.
Drive medical innovation
Be at the forefront of medical innovation by using 3D planning with automated measurements, expert 3D visualization, VR, and more.
Harness the power of 3D
Go beyond 3D visualization and volume rendering with 3D-CT and utilize 3D measurements, automation, AI, simulation, and 3D printing.
How can 3D-CT planning help beyond visualization?
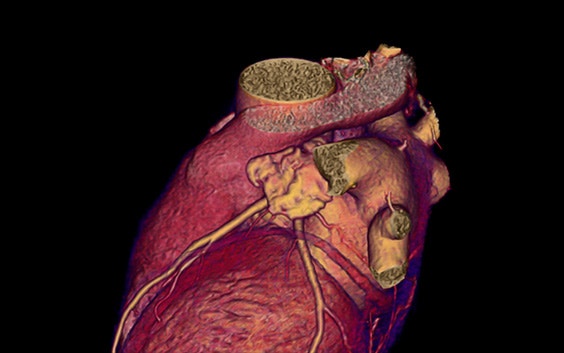
3D volume rendering
“Although a volume render model allows rapid visualization of the grayscale in 3D, it has limited capabilities for downstream operations such as automated quantification.”¹
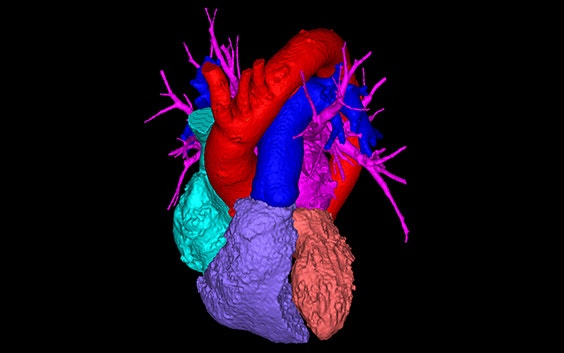
3D-CT planning
“Computational modeling enables automated analysis of anatomic structures, provides enhanced spatial insight and can be converted to a 3D-printed model.”¹
Related products and services
Online case planning assistance for complex structural heart procedures
Online interactive planner for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) procedures
Expert structural heart planning with true 3D clarity for transcatheter mitral valve replacement procedures
Expert structural heart planning with true 3D clarity for left atrial appendage occlusion procedures
Start and scale a sustainable 3D printing lab at your hospital with confidence
Experience effortless online storage and case sharing with this cloud-based collaboration platform.
Accelerate your journey to personalization at scale with the most robust software platform for analysis, planning, and design.
3D-printed cardiovascular models
Clinical evidence
Discover the facts on 3D-CT planning for structural heart interventions
100% procedural success with 3D-CT vs. 92% with 2D-TEE. CT-guided LAAO case planning was associated with improved device selection, accuracy, and procedural efficiency.
Prospective, randomized comparison of 3-dimensional computed tomography guidance versus TEE data for left atrial appendage occlusion (PRO3DLAAO) (2017)
25% reduced procedure time with 3D-CT vs. 2D-TEE. AAO case planning using 3D-CT was significantly more efficient with respect to device utilization, guide catheters, and procedure time.
Prospective, randomized comparison of 3-dimensional computed tomography guidance versus TEE data for left atrial appendage occlusion (PRO3DLAAO) (2017)
75% reduced neo-LVOT assessment time with 3D-CT vs. traditional CT planning. Time to complete neo-LVOT assessment in 2 device positions was found to be between 1 and 5 min.
TCT-440 A More Efficient Method of Patient Evaluation for TMVR: Planning for Best- and Worst-Case Position (2019)
More consistent neo-LVOT prediction with 3D-CT (0.99 ICC) vs. with traditional CT planning (0.87 ICC). With the 3D semi-automatic tool, two modelers estimated a more reliable neo-LVOT area than with the 2D centerline method.
TCT-862 A More Reliable Method for Predicting Neo-LVOT Obstruction after TMVR (2018)

Browse inspiring stories and resources
Discover how others benefit from our structural heart solutions
L-101333-03
Mimics Planner for TAVR makes use of Mimics Cardiac Planner